Class Notes of Chapter 1: Introduction Computer Systems
Part 2
Part 2
Class 11th Informatics Practices
Introduction Computer Systems

Topics:
An ordered set of instructions given to the computer is known as a program and a set of such programs that govern the operation of a computer system and/or its related devices is known as
Software.
Types of Software
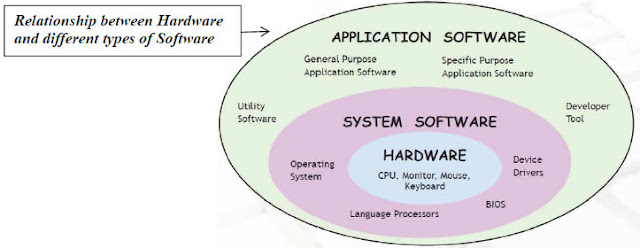
The software can be divided into different types depending upon their uses and application- System Software & Application Software.
Software required to run and maintain basic components of computer system come under the category of system software whereas software required to solve some specific task of daily use is generally called application software.
An operating system is an example of system software while documentation tool, a presentation tool, a spreadsheet tool are all examples of application software. Even your favourite computer game is an example of application software. Some common examples of System Software as follows :
The basic input/output system (BIOS) is also commonly known as the System BIOS. The BIOS is boot firmware, a small program that controls various electronic devices attached to the main computer system. The BIOS sets the machine hardware into a known state to help the operating system to configure the hardware components. This process is known as booting, or booting up. BIOS programs are stored on a chip
2.Operating System
The operating system is a set of system programs that controls and coordinates the operations of a computer system. Operating systems perform all basic tasks, such as identifying basic input/output devices, accepting input from the input devices, sending results to the output devices, keeping track of files and directories on the disk, and controlling other peripheral devices such as disk drives and printers.
Need for an Operating System
The operating system provides a software platform, on top of which, other programs, called application programs are run.
The functions of an operating system can be broadly outlined as follows:
Following types of operating system are generally available and used depending upon the primary purpose and application and the type of hardware attached to the computer:
Allows one user to operate the computer and run different programs on the computer. MS-DOS is a common example of a single-user operating system.
Allows two or more users to run programs at the same time on a single computer system. Unix, Linux, Windows are common examples of the multi-user operating system.
Responds to input instantly. Real-time operating systems are commonly found and used in robotics, complex multimedia and animation, communications and has various military and government uses. LYNX and Windows CE are examples of real-time operating systems.
3.Device Driver
A device driver is a system software that acts as an interface between the Device and the user or the Operating System. All computer accessories like Printer, Scanner, Web Camera, etc come with their own driver software.
4.Language Processor
A computer system understands only machine language or binary language, also known as Low-Level Language(LLL). This language is extremely difficult to learn for a general programmer and thus there is a need for some special language that is easy to learn and understand for the programmer in order to interact with the computer system. These special languages or set of commands are collectively known as programming languages or High-Level languages (HLL).
Some examples of High-Level Programming
Languages are Basic, C, C++, JAVA, etc. These high-level programming languages can easily be translated into machine language using Language Processors. These are:

Topics:
- Types of Software
- System Software
- Application Software
An ordered set of instructions given to the computer is known as a program and a set of such programs that govern the operation of a computer system and/or its related devices is known as
Software.
Types of Software
- System Software
The software can be divided into different types depending upon their uses and application- System Software & Application Software.
Software required to run and maintain basic components of computer system come under the category of system software whereas software required to solve some specific task of daily use is generally called application software.
An operating system is an example of system software while documentation tool, a presentation tool, a spreadsheet tool are all examples of application software. Even your favourite computer game is an example of application software. Some common examples of System Software as follows :
1.BIOS
2.Operating System
The operating system is a set of system programs that controls and coordinates the operations of a computer system. Operating systems perform all basic tasks, such as identifying basic input/output devices, accepting input from the input devices, sending results to the output devices, keeping track of files and directories on the disk, and controlling other peripheral devices such as disk drives and printers.
Need for an Operating System
The operating system provides a software platform, on top of which, other programs, called application programs are run.
The functions of an operating system can be broadly outlined as follows:
- Communicate with hardware and the attached devices [Device Manager]
- Manage different types of memories [Memory Manager]
- Provide a user interface [Interface Manager]
- Provide a structure for accessing an application [Program Manager]
- Enable users to manipulate programs and data [Task Manager]
- Manage the files, folders and directory systems on a computer [File Manager]
Following types of operating system are generally available and used depending upon the primary purpose and application and the type of hardware attached to the computer:
- Single User
Allows one user to operate the computer and run different programs on the computer. MS-DOS is a common example of a single-user operating system.
- Multi-User
Allows two or more users to run programs at the same time on a single computer system. Unix, Linux, Windows are common examples of the multi-user operating system.
- Real Time
Responds to input instantly. Real-time operating systems are commonly found and used in robotics, complex multimedia and animation, communications and has various military and government uses. LYNX and Windows CE are examples of real-time operating systems.
3.Device Driver
A device driver is a system software that acts as an interface between the Device and the user or the Operating System. All computer accessories like Printer, Scanner, Web Camera, etc come with their own driver software.
4.Language Processor
A computer system understands only machine language or binary language, also known as Low-Level Language(LLL). This language is extremely difficult to learn for a general programmer and thus there is a need for some special language that is easy to learn and understand for the programmer in order to interact with the computer system. These special languages or set of commands are collectively known as programming languages or High-Level languages (HLL).
Some examples of High-Level Programming
Languages are Basic, C, C++, JAVA, etc. These high-level programming languages can easily be translated into machine language using Language Processors. These are:
- Assembler: Assembler is a language processor, which translates a program written in assembly language into machine language.
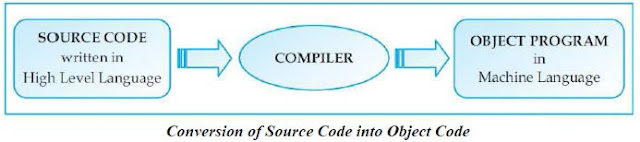
- Compiler: A compiler is a language processor which converts (or translates) the entire program written in a high-level language into machine language in one go.
- Interpreter: This language processor converts a high-level language program into machine language line by line as well as executes it.

- Application Software
Application software is a set of programs to carry out a specific task like the word processor, spreadsheet, presentation tools, library management software, railway reservation, antivirus software, etc. Application Software can be divided into different categories depending upon their uses as follows:
- Utility Software
- General Purpose Application Software
- Specific Purpose Application Software
- Developer Tools
Utility Software
We also require some additional software to keep our computer system efficient and trouble-free. Generally, this software comes bundled with the Operating System Software but we can also use utility software provided by other vendors. Few examples of utility software are as follows:
- Compression Utility Software:- Using this software, you can reduce (compress) the storage size of any computer program/file while not in use.
- Backup Utility Software: Though computer is, in general, a dependable device it is always advisable to take regular back up of important data and programs stored in the computer. In case of any damage to the system, the backup files can be restored and the important data can be recovered from the backup files. This utility software facilitates 14 you to take a regular back-up of important files and folders stored in a drive into another storage device
- Disk De-fragmentation Utility Software: When computer system finds a file too large to store in a single location, it splits the file and stores it in pieces(called fragments), which are logically linked. This simply means that different parts of the file are scattered across the hard drive in noncontiguous locations. Disk de-fragmentation utility software speeds up the system by rearranging such fragmented files stored on a disk in contiguous locations in order to optimize the system performance.
- Antivirus detection and protection software: This utility software provides the user with a virus-free work environment by restricting the entry of any unwanted program into the system.
- Text Editor: This utility software helps one to create, store or edit a basic text file examples of text editors are Notepad, Gedit and K Write
General Purpose Application Software
Some of the application software are designed for general day to day applications and uses. Some of these popular general purpose application software are discussed below: Word
- Processor: Word Processor is general purpose application software that facilitates the creation of text documents with extensive formatting.
- Spreadsheet Tools: Spreadsheet Tool is general purpose application software that facilitates the creation of tabular forms where some text and numerical values can be stored .
- Database Management System: Database Management System is general-purpose application software that facilitates the creation of computer programs that control the creation, maintenance, and the use of dathe tabase for an organization and its end users.
- Specific Purpose Application Software Some: application software are made for performing specific tasks generally used by institutions, corporate, business houses, etc. e.g.
- Inventory Management System & Purchasing System: Inventory Management System is generally used in departmental stores or in an institution to keep the record of the stock of all the physical resources.
- Developer Tools: When a programmer starts the process of writing a program to develop software for any type of application, he/she requires a series of software developing tools like code editor, debugger and compiler. Integrated Development Environment An
Integrated Development Environment
(IDE) is an application program that consists of all required software developing tools required for developing software as part of a single interface. It typically consists of the following tools:
- Source Code Editor
- Graphical User Interface (GUI) builder
- Compiler / Interpreter
- Debugger
- Build Automation tool












No comments:
Post a Comment